|
Background > Sea Ice
Seasonal sea ice cover
Sea ice is characterized by its extent (area), its thickness, and the timing and duration of the ice season. Naturally, the northernmost parts (the Bothnian Sea and Bothnian Bay, as well as the Gulf of Finland) are most strongly affected by sea ice formation. However, there are considerable variations between years. There has been a clear decrease in sea ice extent since the second half of the 20th century, and, remarkably, all winters during the last 10 years have been milder than average.
The seasonal ice cover of the Baltic Sea influences the energy transfer between the sea surface and the atmosphere. It provides a habitat for the Baltic RInged Seal and has long been important for winter navigation and travel across the Baltic Sea.
Sea ice animations
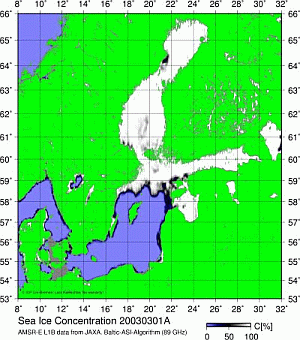
Animations of the seasonal ice cover are available for the winters:
Winter 2002/2003
Winter 2003/2004
Winter 2004/2005
Winter 2005/2006
Winter 2006/2007
Winter 2007/2008
|

